-
Valve definition and classification!
Valve is a fluid pipeline control device, its basic function is to connect or cut off the flow of pipeline medium, change the flow direction of the medium, adjust the pressure and flow of the medium, to protect the normal operation of pipeline equipment. The valve is usually composed of the valve body, valve cover, seat, opening and closing parts (disc, gate, disc and diaphragm, etc.), driving mechanism (valve stem and valve drive device that drives its movement), seals (packing, gasket, etc.) and fasteners. Valve is a fluid pipeline control device, its basic function is to connect or cut off the flow of pipeline medium, change the flow direction of the medium, adjust the pressure and flow of the medium, to protect the normal operation of pipeline equipment. The valve is usually composed of the valve body, valve cover, seat, opening and closing parts (disc, gate, disc and diaphragm, etc.), driving mechanism (valve stem and valve drive device that drives its movement), seals (packing, gasket, etc.) and fasteners.
Valve classification
Valves have a wide range of uses, a wide variety of classification methods are also more.
1.1 By drive
Automatic valve: A valve that relies on the ability of the medium (liquid, gas, etc.) to act on its own. Such as check valves, safety valves, regulating valves, steam traps, pressure reducing valves, etc.
Drive valve: With manual, electric, hydraulic, pneumatic to operate the action of the valve. Such as gate valve, globe valve, butterfly valve, ball valve, plug valve and so on.
(1) Manual valve: with the help of hand wheel, handle, lever or sprocket, etc., the valve is operated by manpower, when the transmission of large torque, worm gear, gear and other decelerating devices can be used.
(2) Electric valves: valves operated by electric motors, electromagnetic or other electrical devices.
(3) Hydraulic: driven by (water, oil).
(4) Pneumatic: driven by compressed air

1.2 According to pressure
Low pressure: various valves with nominal pressure less than 1.6MPa.
Medium pressure valve: nominal pressure of 2.5-6.4mpa of various valves.
High pressure valve: nominal pressure 10-80mpa of various valves.
Ultra-high pressure valves: all kinds of valves with nominal pressure greater than 100MPa.

1.3 temperature-wise
High temperature valve t > 450℃ valve
Medium temperature valve 120 ℃≤ t ≤ 450℃ valve
Normal temperature valve -29℃ ≤ t ≤ 120℃ valve
Low temperature valve -100℃≤ t ≤ -29℃ valve
Ultra-low temperature valve t < -100℃ valve
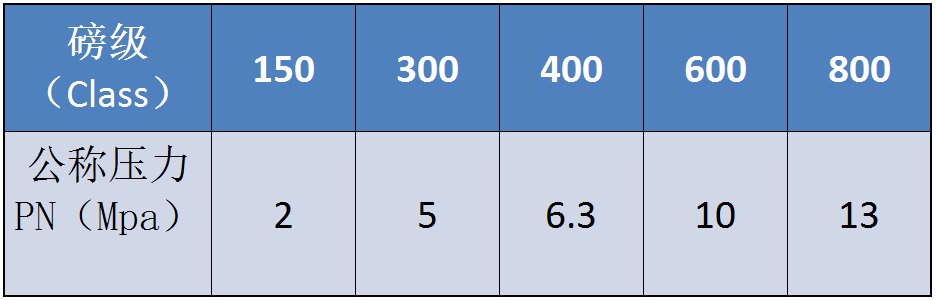
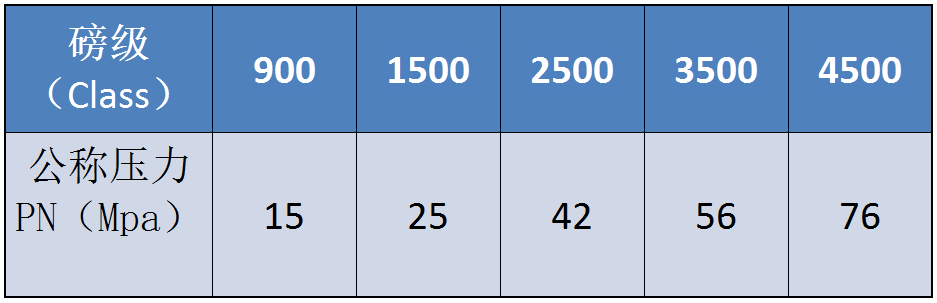
1.4 Classification by nominal size
Small diameter valve nominal size DN≤40mm valve
Medium diameter valve nominal size DN50--300mm valve
Large diameter valve nominal size DN350- 1200mm valve
Large diameter valve nominal size DN≥1400mm valve
1.5 According to the connection with the pipeline can be divided into
Flanged valve: Valve body with a flange, and the pipe using a flange connection valve.
Threaded valve: Valve with internal or external threads in the body and threaded to the pipe.
Welded valve: Valve body with a welding port, welded to the pipe connection valve.
Clamp connected valve: Valve with clamp on the valve body and connected with the pipe by the clamp
Sleeve connected valve: A valve connected with a pipe by a sleeve.
1.6 By purpose
Cut-off valves: mainly used to connect or cut off the medium in the pipeline, such as gate valves, globe valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, etc.
Check valves: Used to prevent the backflow of the medium, such as check valves.
Regulating valves: mainly used to regulate the pressure and flow of the pipeline medium, such as regulating valves, regulating valves, pressure reducing valves.
Diverter valve type: used to change the flow direction of the medium in the pipeline, play the role of distributing and diverting the medium, such as three-way cock, distributing valve, slide valve, etc.
Safety valve: When the medium pressure exceeds the specified value, it is used to discharge excess media to ensure the safety of pipeline systems and equipment, such as safety valves and accident valves.
Other special valves: such as steam trap, blowdown valve, blowdown valve, etc.




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)